The Science of Emotional Resilience: How Your Brain Handles Stress

Emotional resilience is the brain’s ability to adapt to stress and trauma, involving neuroplasticity and specific brain regions, and it can be enhanced through various strategies, promoting mental well-being.
Discover the science of emotional resilience: understanding the brain’s response to stress and trauma, and learn how to fortify your mind against life’s inevitable challenges, paving the way for greater well-being.
Understanding the Neuroscience of Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience is not just a vague concept; it’s deeply rooted in neuroscience. Understanding the neural mechanisms involved can provide valuable insights into how we can improve our ability to cope with adversity.
Let’s delve into the key brain regions and processes that contribute to emotional resilience, shedding light on the biological foundations of this crucial skill.
The Role of the Amygdala and Hippocampus
The amygdala and hippocampus play pivotal roles in processing emotions and memories, respectively. How these regions interact under stress significantly impacts emotional resilience.
The amygdala is responsible for processing emotions, particularly fear and anxiety. The hippocampus is involved in memory formation and contextualizing emotional experiences.
- Amygdala Regulation: Resilient individuals often exhibit better regulation of the amygdala, preventing excessive fear responses.
- Hippocampal Function: A healthy hippocampus helps in contextualizing stressful events, reducing their emotional impact.
- Neural Pathways: Stronger connections between the prefrontal cortex and these regions facilitate better emotional control.
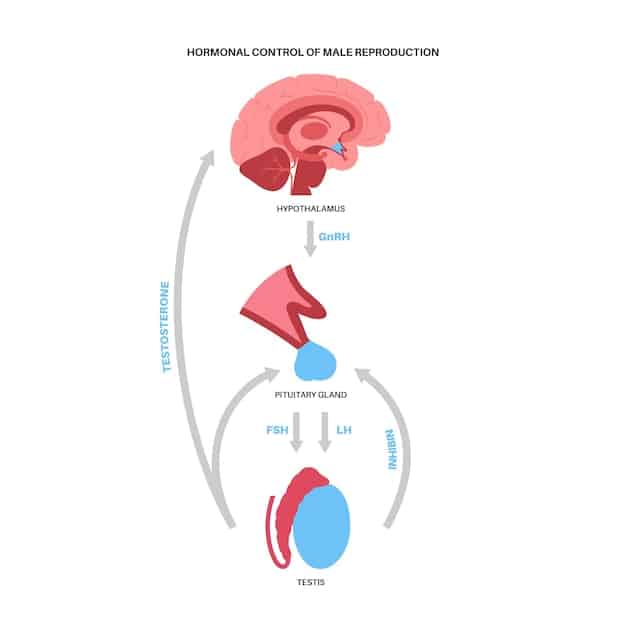
In essence, resilience involves a balanced interplay between emotional reactivity (amygdala) and cognitive processing (hippocampus and prefrontal cortex), allowing for adaptive responses to stress.
Neuroplasticity: The Brain’s Capacity for Change
Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life, is fundamental to emotional resilience. This capacity allows us to adapt and recover from traumatic experiences.
Understanding neuroplasticity can empower us to actively shape our brains and cultivate resilience through targeted practices and experiences.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify its connections or re-wire itself. Without this remarkable ability, the brain would be unable to develop from infancy through adulthood or recover from brain injury.
How Neuroplasticity Supports Resilience
Neuroplasticity enables the brain to recover from trauma and adapt to new challenges, fostering resilience in the face of adversity.
- New Neural Pathways: Forming new connections that support positive coping mechanisms is crucial for resilience.
- Weakening Negative Associations: Neuroplasticity can help weaken associations between stimuli and negative emotional responses.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Learning to reframe thoughts and beliefs can alter neural pathways, promoting more adaptive thinking.
By leveraging neuroplasticity through practices such as mindfulness and cognitive therapy, individuals can actively rewire their brains to become more resilient over time.
The Impact of Stress on Brain Function
Chronic stress can have a detrimental impact on brain function, impairing cognitive abilities and emotional regulation. Understanding these effects is vital for developing effective resilience strategies.
Stress hormones, such as cortisol, can disrupt neural pathways and compromise the integrity of brain regions involved in emotional processing.
Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can shrink the hippocampus, which can affect emotions. These impacts can be reversed by strategies that activate nerve growth.
Stress Hormones and Their Effects
Stress hormones like cortisol can disrupt brain function, impairing cognitive abilities and emotional regulation.
Elevated cortisol levels can damage neurons in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, disrupting their normal function. This can lead to difficulties in memory, decision-making, and emotional control.
- Impaired Cognition: Chronic stress can reduce cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Stress can exacerbate anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
- Reduced Neuroplasticity: High stress levels hinder the brain’s ability to form new connections and adapt to change.
Therefore, managing stress through techniques like exercise, meditation, and social support is crucial for protecting brain health and fostering emotional resilience.
Strategies to Enhance Emotional Resilience
Fortunately, there are many effective strategies to enhance emotional resilience and promote brain health. These approaches include both psychological and lifestyle interventions.
By incorporating these practices into our daily lives, we can strengthen our ability to cope with stress and adversity, fostering greater well-being and resilience.
Lifestyle changes, mental habits, mindsets, behaviors and methods of dealing with both internal and external stressors are all strategies to help you to become more emotionally resilient.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices can help regulate emotions, reduce stress, and enhance self-awareness, thereby fostering resilience.
These practices involve focusing attention on the present moment without judgment, allowing individuals to observe their thoughts and feelings without getting carried away by them.
Mindfulness meditation is a mental training practice that teaches you to slow down racing thoughts, let go of negativity, and calm both your mind and body.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a proven therapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors, thereby improving emotional resilience.
- Identifying Negative Thoughts: Recognizing and challenging maladaptive thoughts is a key component of CBT.
- Behavioral Activation: Engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment can boost mood and resilience.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Developing effective problem-solving strategies can reduce stress and improve coping abilities.
By learning to reframe negative thoughts and cultivate more adaptive coping strategies, individuals can enhance their emotional resilience and improve their overall mental well-being.
The Role of Social Support in Building Resilience
Social support plays a vital role in building emotional resilience, providing individuals with a sense of belonging, validation, and assistance during challenging times.
Strong social connections can buffer the negative effects of stress, promote positive emotions, and enhance coping abilities.
The quality and amount of social support can play a big part in your emotional wellbeing. If you have a diverse group of friendships and relationships, you’re more likely to be resilient when facing adversity.
The Benefits of Social Connections
Strong social connections can buffer the negative effects of stress, promote positive emotions, and enhance coping abilities.
- Emotional Validation: Sharing feelings and experiences with others can provide validation and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Practical Assistance: Receiving support from others can alleviate stress and provide resources for coping with challenges.
- Enhanced Sense of Belonging: Feeling connected to others fosters a sense of purpose and meaning, promoting greater emotional resilience.
Therefore, nurturing social connections and seeking support from others are essential components of building emotional resilience and promoting overall well-being.
Lifestyle Factors and Brain Health
Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and sleep play a crucial role in promoting brain health and enhancing emotional resilience. These lifestyle choices can directly impact the structure and function of the brain, influencing mood, cognition, and stress response.
Proper nutrition provides the building blocks for neurotransmitters and neural connections, while regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain and promotes neuroplasticity. Adequate sleep allows the brain to consolidate memories and recharge, reducing vulnerability to stress.
Leading a healthy lifestyle by making sure you’re sleeping well, eating nutritious foods and exercising will make you more resilient to stress.
The Impact of Diet, Exercise, and Sleep
Diet, exercise, and sleep are essential lifestyle factors that can significantly impact brain health and emotional resilience.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids provides the nutrients necessary for optimal brain function.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, promoting neuroplasticity and reducing stress.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep allows the brain to consolidate memories and recharge, reducing vulnerability to stress.
| Key Concept | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠 Neuroplasticity | The brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. |
| 🧘 Mindfulness | A practice that enhances emotional regulation and reduces stress through present moment awareness. |
| 💪 Social Support | The network of relationships providing emotional and practical assistance during tough times. |
| 😴 Adequate Sleep | Essential for brain repair and reducing stress vulnerability. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Emotional resilience is the ability to bounce back from difficult experiences. It involves adapting well in the face of adversity, trauma, tragedy, threats, or significant sources of stress.
▼
Stress can impact cognitive function and emotional regulation by disrupting neural pathways and affecting brain regions like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, leading to impaired memory and decision-making.
▼
Yes, emotional resilience can be improved through various strategies, including mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), social support, and lifestyle changes that promote brain health.
▼
Neuroplasticity allows the brain to form new connections and adapt to changes, which is essential for recovering from trauma and developing new coping mechanisms that support emotional resilience.
▼
Social support provides validation, reduces isolation, and offers practical assistance, buffering the negative effects of stress and enhancing an individual’s ability to cope with adversity, fostering greater resilience.
Conclusion
Understanding the science of emotional resilience: understanding the brain’s response to stress and trauma provides valuable insights into how we can cultivate and enhance our ability to cope with life’s challenges. By knowing and applying strategies that promote brain health and foster resilience, we can empower ourselves to navigate adversity and thrive in the face of stress, ultimately leading to greater well-being and fulfillment.





